Motivation, the driving force that propels us into action, has been the subject of fascination for centuries. In this exploration, we will dissect various motivation theories to uncover the underlying principles that influence our behavior. From the classics to the contemporary, let’s delve into the realm of motivation and understand how these theories shape our aspirations, goals, and ultimately, our achievements.
1. Decoding Motivation Theories: A Roadmap to Success
Motivation theories serve as guiding frameworks that help explain why individuals behave the way they do. These theories provide insights into the factors that drive us toward specific goals and outcomes. As we navigate through the intricate world of motivation, let’s explore some key theories that have stood the test of time.
2. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Building Blocks of Motivation
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a foundational theory that outlines the fundamental elements driving human motivation. At the base of the pyramid lie physiological needs, such as food and shelter, followed by safety, love and belonging, esteem, and finally, self-actualization at the pinnacle. According to Maslow, individuals strive to fulfill these needs sequentially, with higher-level needs becoming prominent once lower-level ones are satisfied.
Understanding Maslow’s theory provides a lens through which we can view the varied motivations that guide human behavior. For example, an individual struggling to meet basic physiological needs may prioritize securing a stable job or source of income over pursuing self-actualization through creative endeavors.
3. Expectancy Theory: Anticipating Success Through Effort
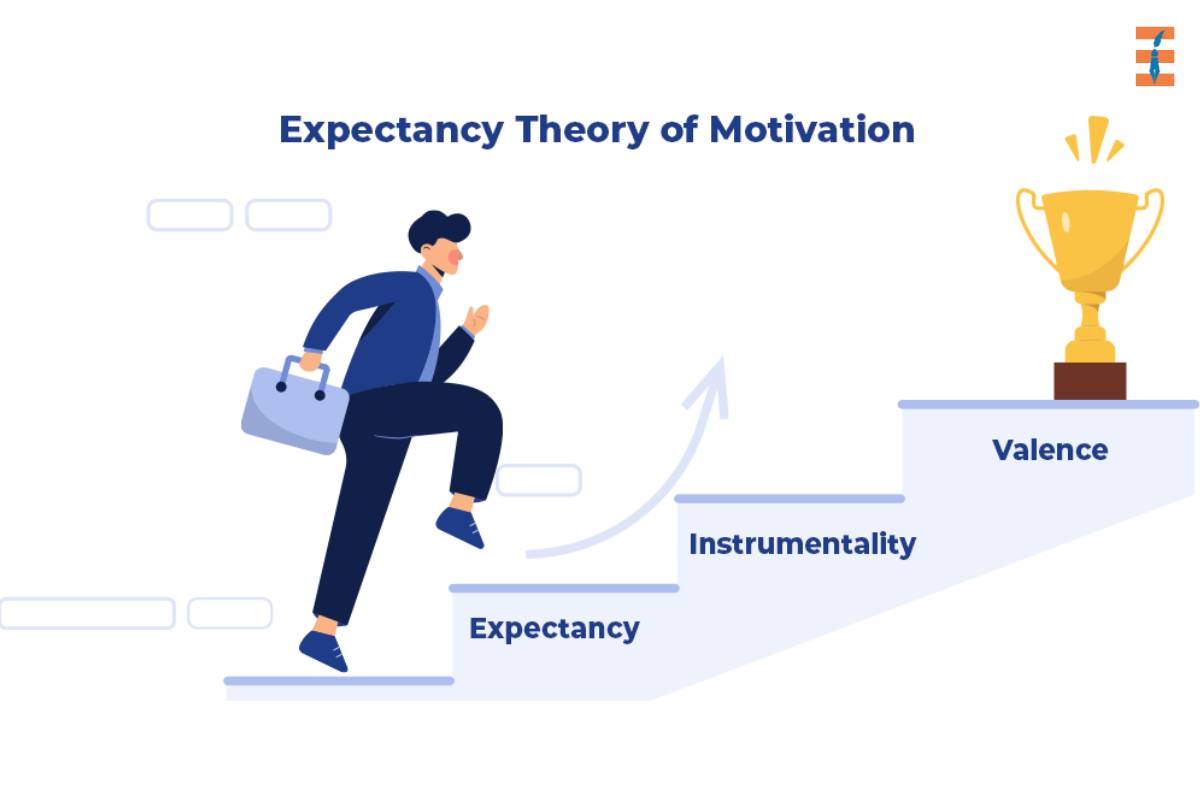
Victor Vroom’s Expectancy Theory revolves around the belief that people are motivated to act in a certain way if they believe their efforts will lead to a desired outcome. This theory takes into account three key factors: expectancy, instrumentality, and valence.
- Expectancy: The belief that effort will lead to performance.
- Instrumentality: The belief that performance will lead to rewards.
- Valence: The value an individual places on the anticipated rewards.
By understanding these components, organizations can tailor motivational strategies to align with employees’ expectations and maximize performance.
4. Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory: Unraveling Job Satisfaction
Frederick Herzberg’s Two-Factor Motivation theory distinguishes between hygiene factors and motivators in the workplace. Hygiene factors, such as salary and working conditions, prevent dissatisfaction but do not necessarily motivate. On the other hand, motivators, like recognition and opportunities for growth, contribute to job satisfaction and increased motivation.
Applying Herzberg’s theory in organizational settings involves addressing both hygiene factors and motivators to create a work environment that not only prevents dissatisfaction but also fosters employee engagement and enthusiasm.
5. Self-Determination Theory: The Quest for Autonomy

Edward Deci and Richard Ryan’s Self-Determination Theory posits that individuals are inherently motivated to meet their psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness. This theory emphasizes the importance of intrinsic motivation, where individuals engage in activities for the inherent satisfaction they provide rather than external rewards.
Understanding Self-Determination Theory can guide educators, employers, and leaders in creating environments that support individuals’ innate drive for autonomy, competence, and connection.
6. Goal-Setting Theory: Charting the Course to Achievement
First introduced by Edwin Locke, the Goal-Setting Theory asserts that specific and challenging goals lead to higher levels of motivation and performance. According to this theory, individuals are more likely to be motivated when they have clear objectives that require effort and commitment.
Applying Goal-Setting Theory involves setting SMART goals – specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Whether in personal development or organizational management, this theory provides a roadmap for translating aspirations into actionable steps.
7. Applying Motivation Theories in Everyday Life

Understanding motivation theories goes beyond theoretical knowledge; it involves applying these principles to enhance our daily lives. Here are some practical tips:
- Set Clear Goals: Apply Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory by defining specific, challenging goals for personal and professional growth.
- Recognize Intrinsic Motivation: Acknowledge activities that bring intrinsic satisfaction and prioritize them in your daily routine.
- Address Workplace Motivators: Organizations can boost employee motivation by recognizing and incorporating Herzberg’s motivators, such as recognition and opportunities for advancement.
- Foster Autonomy: Encourage autonomy in personal and professional pursuits, aligning with the principles of Self-Determination Theory.
- Create a Motivating Environment: Consider Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs when evaluating personal and organizational priorities, ensuring fundamental needs are met before striving for higher-level goals.
8. Challenges in Applying Motivation Theories
While motivation theories offer valuable insights, their application is not without challenges. Individuals are unique, and motivational factors can vary widely. Recognizing this diversity is essential to effectively applying these theories in different contexts.
Moreover, external factors such as cultural influences, societal expectations, and economic conditions can impact the applicability of motivation theories. Successful implementation requires flexibility and a nuanced understanding of the specific environment in which these theories are applied.
Conclusion: Decoding Motivation Theories
Motivation theories serve as invaluable tools in unraveling the complexities of human behavior. From Maslow’s basic needs to Vroom’s expectancy considerations, each theory provides a distinct perspective on what drives us to take action. By incorporating these theories into our understanding, we gain insights that can guide personal development, organizational management, and the pursuit of lifelong aspirations.
As we navigate the motivational matrix, let’s remember that theories, though powerful, are mere guides. The true journey lies in the application of these principles in our daily lives, shaping our motivations, aspirations, and ultimately, our achievements.
FAQs
1. Can motivation theories be universally applied?
Ans: While these theories offer valuable insights, their application may vary based on individual differences, cultural factors, and environmental conditions.
2. How can organizations use motivation theories to enhance workplace culture?
Ans: Organizations can apply these theories by recognizing and addressing employees’ intrinsic motivators, setting clear goals, and fostering a motivating work environment.
3. What role does autonomy play in motivation?
Ans: Autonomy is a crucial factor in motivation, as highlighted by the Self-Determination Theory. Providing individuals with choices and control over their actions enhances intrinsic motivation.
4. Are there any drawbacks to setting challenging goals, as suggested by Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory?
Ans: Setting challenging goals can enhance motivation, but unrealistic or excessively difficult goals may lead to frustration and demotivation. It’s essential to strike a balance and ensure goals are achievable.
5. How can individuals overcome motivational challenges in their personal lives?
Ans: Individuals can overcome motivational challenges by understanding their unique drivers, setting realistic goals, seeking intrinsic satisfaction, and creating a supportive environment that aligns with their values and aspirations.
Also Read:15 Isaac Newton Quotes That Will Ignite Your Curiosity

