What if education were catered to all aspects of a student’s life? Can focusing on each individual help them grow into well-rounded adults?
The Humanistic Learning Theory is an approach in education that looks at the whole person, not just their grades.
While traditional models focus on memorizing facts and following behavioral rules, this theory is different. It highlights personal growth, reaching your full potential, and caring for the learner’s feelings and well-being.
Humanistic learning is based on the idea that students learn best when they feel valued and supported. Learning becomes more meaningful and engaging when teachers notice each student’s needs and experiences. Students not only gain knowledge but also grow in confidence, creativity, and self-awareness. In this article, we will explore the key features of Humanistic Learning Theory, ways teachers can use it in the classroom, and its main advantages and disadvantages.
What is Humanistic Learning Theory?
Humanistic Learning Theory was developed by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers in the mid-20th century. They wanted learning to focus on the whole person, not just memorizing facts or scoring well on tests.
Maslow is famous for his hierarchy of needs. He said people must meet basic needs like food, safety, and belonging before they can grow and learn effectively. In schools, this means you will learn better when you feel safe, valued, and supported. Rogers added another idea: teachers should act as guides, not strict rulers. He believed learners should have freedom and choice in their learning. When students feel respected and understood, they become more curious, creative, and motivated.
Humanistic learning focuses on personal growth, self-discovery, and curiosity. You are encouraged to ask questions, explore ideas, and learn at your own pace. Emotions, social skills, and personal values are just as important as cognitive skills. Learning is not only about memorizing facts; it’s about understanding yourself and the world around you.
This theory also values empathy and respect. A supportive classroom helps you feel confident and motivated. It encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and self-reflection. When applied well, humanistic learning can make education more engaging and meaningful. You develop not just knowledge but also creativity, independence, and confidence.
There are a few key features of humanistic learning. They act as guidelines around which the theory is built. Let us now learn more about them.
Also Read: Hard Skills vs Soft Skills: Which Matters More for Career Growth?
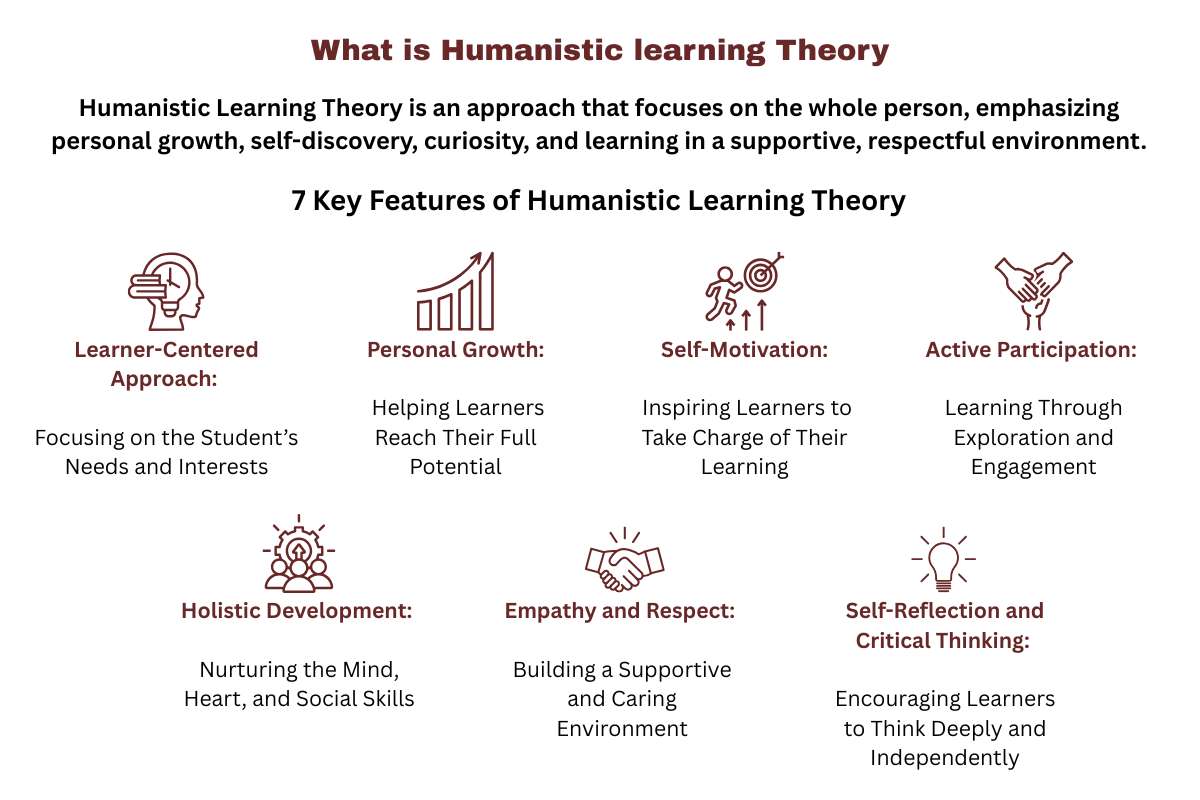
7 Key Features of Humanistic Learning Theory
1. Learner-Centered Approach:
Humanistic learning puts the learner at the center. His or her needs, interests, and feelings guide the learning process, rather than rigid rules or memorization. Teachers do not force them to follow strict rules or memorize everything.
2. Personal Growth:
The theory focuses on developing your full potential. Learning isn’t just about knowledge; it’s about becoming a more confident, creative, and capable person. Students should develop skills like communication and self-awareness.
3. Self-Motivation:
Students are encouraged to take charge of their learning. Motivation comes from curiosity and personal goals, not just rewards or punishments.
4. Active Participation:
Learning is not just listening or copying notes. It is interactive. You explore, ask questions, and solve problems instead of passively listening or copying information.
5. Holistic Development:
Humanistic learning theory considers a child’s emotions and values. It also focuses on social skills along with cognitive growth. Education is about shaping the whole person.
6. Empathy and Respect:
A supportive environment is key. Teachers and peers show understanding and respect, which helps a student feel safe and confident in learning.
7. Self-Reflection and Critical Thinking:
Children are encouraged to reflect on experiences and think deeply about ideas. This develops independence, problem-solving skills, and a better understanding of yourself.
Implement Humanistic Learning Theory in These 5 Ways
Teachers and mentors can use this theory to shape students’ mentality. They can prepare them for the future. Humanistic Learning can be implemented in the following ways:
1. Flexible Lesson Plans
Teachers can adapt lessons to meet students’ needs and interests. For example, if a student enjoys technology, include apps, videos, or coding exercises. Flexibility also means adjusting the pace for students who need more time. You can also offer extra challenges for advanced learners. When lessons connect to students’ lives, they become more motivated and engaged. Flexible plans also allow teachers to respond to students’ questions and curiosity as they arise.
Key Takeaway: Teaching should adapt to students’ interests, needs, and learning pace.
2. Project-Based Learning

Project-based learning helps students explore real-world problems. For example, in science, students could create a small garden, watch how plants grow, or start a recycling project. These projects help students use what they learn in real life. They also build teamwork, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Students get a chance to take charge of their learning, see their results, and feel proud of what they achieve.
Key Takeaway: Students learn best through hands-on experiences that connect learning to real life.
Also Read: What is Project-Based Learning?
3. Interactive Discussions
Encouraging discussions gives students space to share their thoughts and ideas. After reading a story, teachers can ask students what they would do in a character’s place or how the story relates to real life. Discussions help students build confidence, critical thinking, and communication skills. Teachers can guide conversations to ensure every student participates and learns from others’ perspectives.
Key Takeaway: Learning is deepened when students actively express ideas, reflect, and engage with others.
4. Mentorship and Guidance
Teachers can provide one-on-one support to help students meet personal goals. For example, checking in weekly allows students to plan learning activities, reflect on challenges, or set new targets. Mentorship creates trust, motivates students, and helps them take responsibility for their growth. Personalized guidance also helps students feel valued and understood.
Key Takeaway: Individualized guidance helps learners set goals, overcome challenges, and take ownership of their development.
5. Incorporate Arts and Creativity
Humanistic learning can also be used with activities like music, drawing, drama, or storytelling. For example, students could create a comic to explain a science idea or write a short play about history. These activities make learning creative and fun. Creative tasks encourage imagination, self-expression, and engagement. They also make learning enjoyable and memorable.
Key Takeaway: Encouraging creative activities nurtures imagination, emotional expression, and deeper understanding.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Humanistic Learning Theory

Just like any other method of teaching, this theory has both pros and cons. These include:
Strengths:
1. Focus on the Whole Student
It values emotions, creativity, and social growth along with academics. This helps students develop life skills, not just knowledge.
2. Boosts Motivation and Confidence
Giving students freedom and choice makes learning feel personal. Students stay motivated and gain confidence in their abilities.
3. Encourages Independent Thinking
Students learn to reflect, make decisions, and solve problems. This builds independence and prepares them for real-world challenges.
Weaknesses:
1. Hard to Measure Progress
Since learning focuses on personal growth, it is difficult to measure with traditional tests or grades. Some students may struggle without clear benchmarks.
2. Time-Consuming for Teachers
Designing flexible lessons, guiding discussions, and offering individual support can take more time compared to traditional methods.
3. May Not Fit All Learning Styles
Some students need more structure and direct instruction. Too much freedom may cause confusion or a lack of focus.
Conclusion:
The Humanistic Learning Theory shows us that learning is more than just books and exams. It focuses on the whole person, including their feelings, goals, and growth.
This approach helps students feel supported, valued, and motivated to learn. By making education more personal, it builds confidence and helps learners connect lessons to real life. In short, humanistic learning makes education meaningful and lasting.
FAQ
1. How is this theory used in schools?
Teachers use it by giving students choices, encouraging self-study, and creating a caring classroom.
2. What are some examples of Humanistic Learning activities?
Activities like group discussions, self-reflection exercises, and creative projects help students learn while building confidence and self-awareness.
3. How does it help shy or struggling students?
Creating a supportive environment helps them feel safe, valued, and more willing to participate and try new things.

